
Chinese hackers compromised over 20,000 Fortinet devices in 2022-2023, breaching “a large number of companies within the defense industry.”
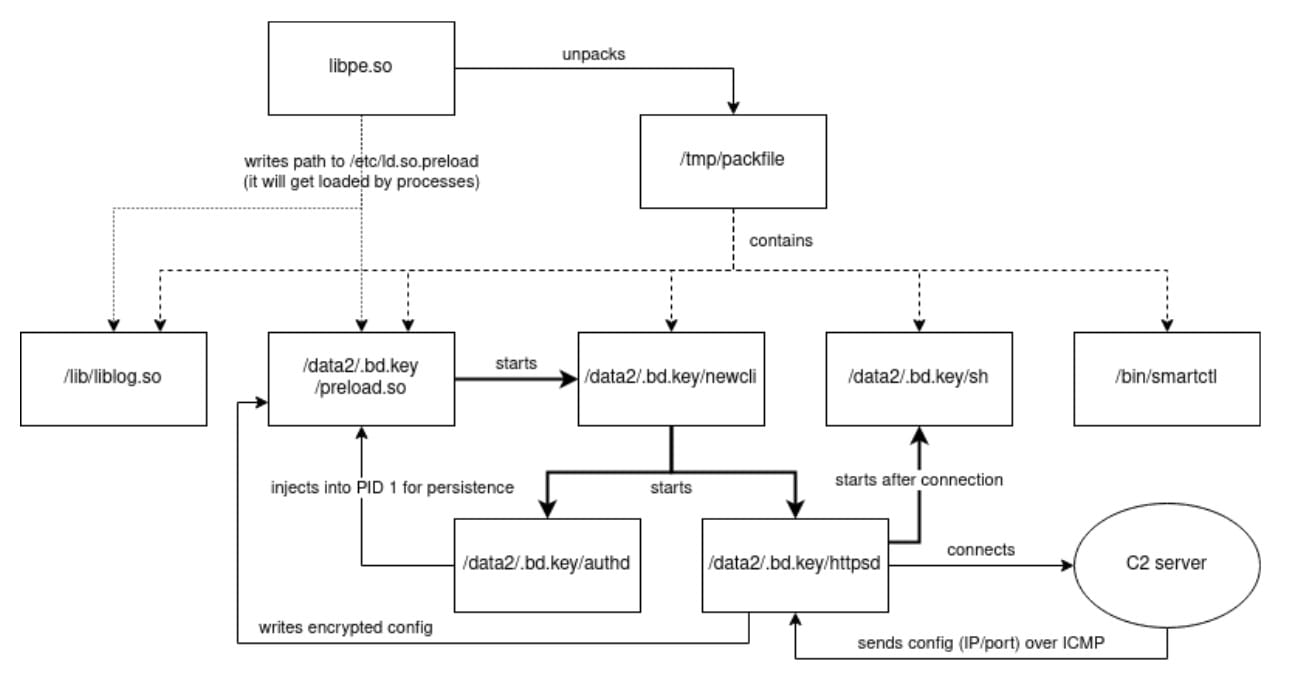
They exploited a previously unseen, bespoke malware for Fortinet devices dubbed COATHANGER that “survives reboots and firmware upgrades.”
That’s according to the Dutch cybersecurity agency NCSC this week – which said its earlier February alert – published alongside the country’s Ministry of Defence (MoD) – had underestimated the scale of the campaign.
The NCSC added in a June 10 update that the difficulty of removing the persistent secondary stage malware means the threat group likely still has access to the system of a “significant” number of victims.
Fortinet “COATHANGER” attacks worse than thought
The attackers compromised 14,000 Fortinet devices (firewalls and VPNs) two months before the software and hardware vendor apushed a fix for the critical vulnerability (CVE-2022-42475) that the attackers had been using for initial access. They then continued hitting unpatched devices.
The secondary stage malware (COATHANGER) gave them persistence.
Holland’s MoD was among the victims. It said only a network for unclassified projects was breached and due to effective network segmentation, the attackers were blocked from moving to other systems.
It earlier noted that “although this incident started with abuse of CVE-2022-42475, the COATHANGER malware could conceivably be used in combination with any present or future software vulnerability in FortiGate devices” (of which there has been no widely exploited shortage; e.g CVE-2024-21762 and CVE-2024-23113 or CVE-2023-48788 or… )
Given a proliferation of zero days and widespread exploitation of appliances like those targeted in this campaign, the NCSC said it “it is important that organizations practice the ‘assume breach’ principle.”
The only currently identified way of removing COATHANGER from an infected FortiGate device involves formatting the device and reinstalling and reconfiguring the device. The Dutch MOD notes that “several methods have been identified to detect COATHANGER implants.
“These include a YARA-rule, a JA3-hash, different CLI commands, file checksums and a network traffic heuristic.” Further IOCs are here.
